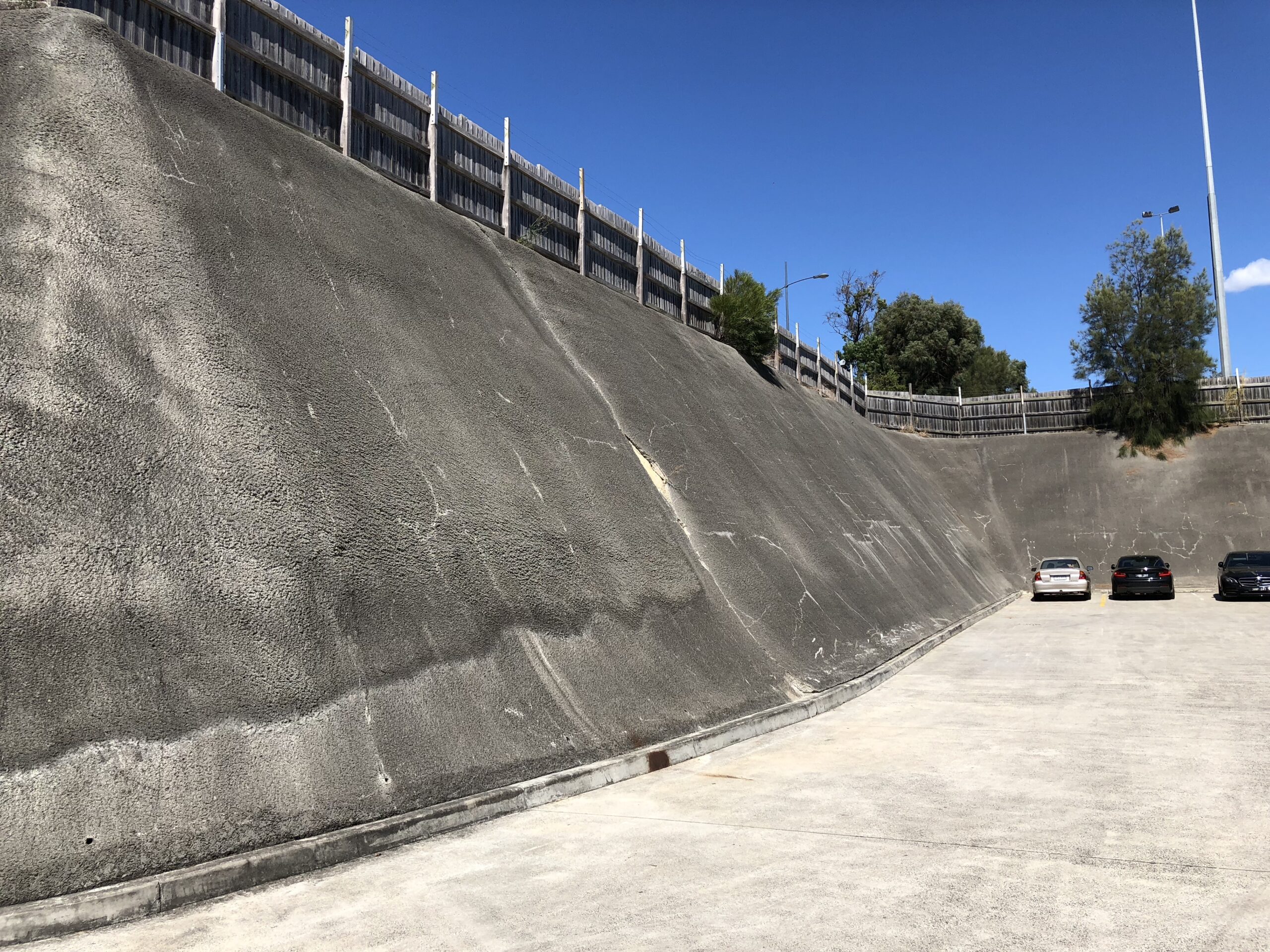

Slope Stability Assessment is the potential of a naturally occurring or engineered soil slope (i.e., embankments, cuttings, open-pit mining, excavations, landfills, etc.) to withstand ground movement. A previously stable slope may become unstable, leading to mass movement. Mass movements can be caused by an increase in shear stress, like increased loading or lateral pressure. Shear strength may also be decreased by the effects of weathering or changes in pore water pressure.
Slope stability analysis is the investigation of potential failure mechanisms and the sensitivity to various triggering mechanisms. Slope stability analysis involves the design of optimal slopes with regard to safety, reliability and economics and the design of possible remedial measures.
Slope design requires geological information and site characterisation, for example: soil or rock properties; slope geometry; and groundwater conditions. The presence of water causes an extremely detrimental effect on slope stability. Water pressure within the pore spaces, fractures or other discontinuities will reduce the shear strength.
For weak or unstable slopes, a comprehensive intrusive geotechnical investigation together with assessment and monitoring is required to provide a sustainable solution. The design and scope for a suitable slope stability investigation will consider the soil and groundwater conditions; stability of existing slopes; design of new cuttings and embankments; and monitoring slope movement.
Oz Geos has experience with the design and management of site investigations involving slope stability analysis. Our geotechnical engineering team can provide advice and recommendations for the design and construction for new slopes, cuttings and embankments or the remediation of failed slopes.
Using data obtained from the intrusive ground investigation Oz Geos can provide advice on the design of schemes to improve slope stability to permit development. Using finite element analysis software we can assess the stability of existing slopes and the effect a proposed development will have upon the factor of safety against failure.

 CIVIL ENGINEERING
CIVIL ENGINEERING ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT
ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENT GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING
STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING























